Classroom management and behavior management are related concepts in the context of education, but they focus on different aspects of creating a conducive learning environment. Here’s a detailed explanation of each and their differences:
Classroom Management
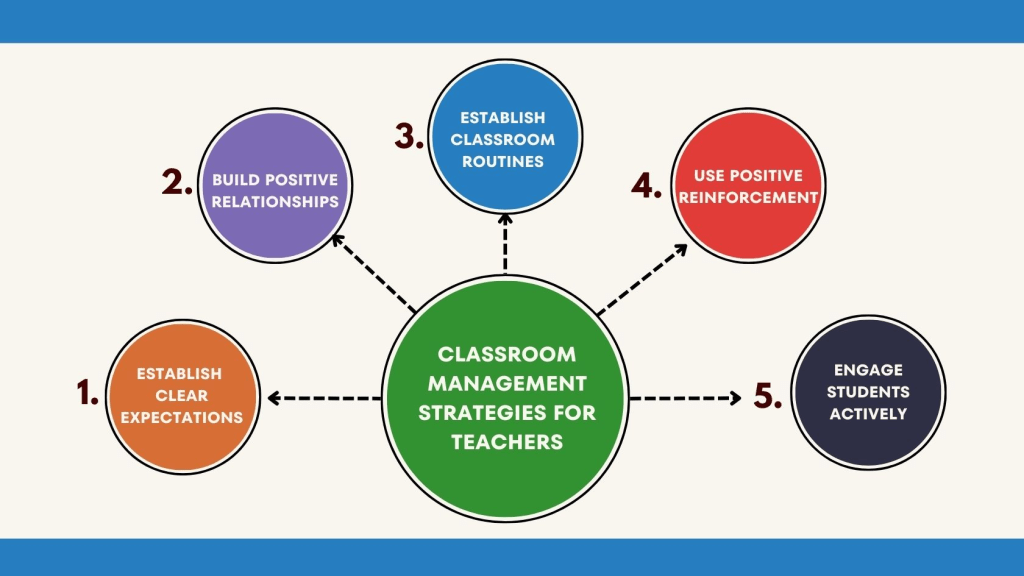
Classroom Management refers to the overall process of organizing and controlling the classroom environment to promote effective teaching and learning. It encompasses a wide range of strategies and practices aimed at creating a positive and productive learning atmosphere. Key components include:
- Physical Arrangement: Organizing the physical space to enhance learning, such as seating arrangements, accessibility, and classroom decor.
- Routine and Procedures: Establishing consistent routines and procedures to provide structure and predictability.
- Instructional Techniques: Employing various teaching methods and strategies to engage students and facilitate learning.
- Time Management: Efficiently managing classroom time to maximize learning opportunities.
- Relationship Building: Fostering positive relationships between the teacher and students, and among students themselves.
- Motivation and Engagement: Using strategies to motivate and engage students in the learning process.
Behavior Management
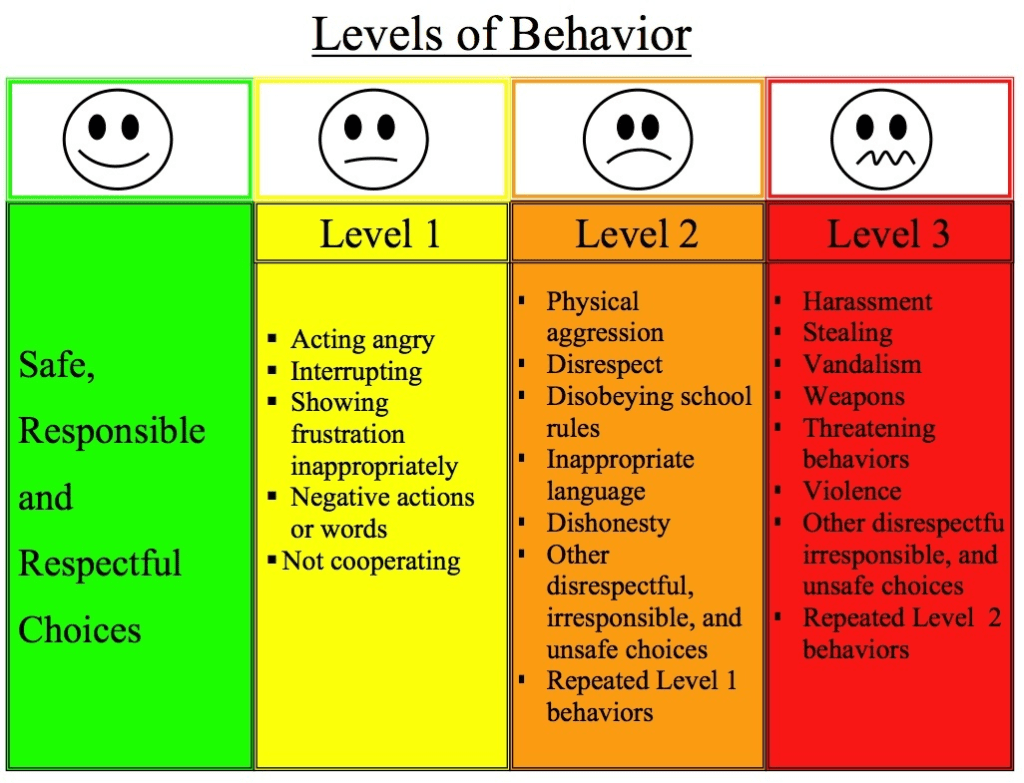
Behavior Management focuses specifically on addressing and modifying student behavior to ensure a safe and conducive learning environment. It involves the use of techniques and interventions to promote positive behavior and reduce or eliminate disruptive behavior. Key components include:
- Behavioral Expectations: Clearly defining and communicating behavioral expectations to students.
- Positive Reinforcement: Using rewards and positive reinforcement to encourage desirable behavior.
- Consequences: Implementing consistent consequences for undesirable behavior to discourage it.
- Behavioral Interventions: Applying specific interventions and strategies to address individual or group behavior issues.
- Social-Emotional Learning: Teaching and promoting social-emotional skills to help students manage their emotions and interactions.
- Conflict Resolution: Implementing strategies to resolve conflicts and promote positive interactions.
Key Differences
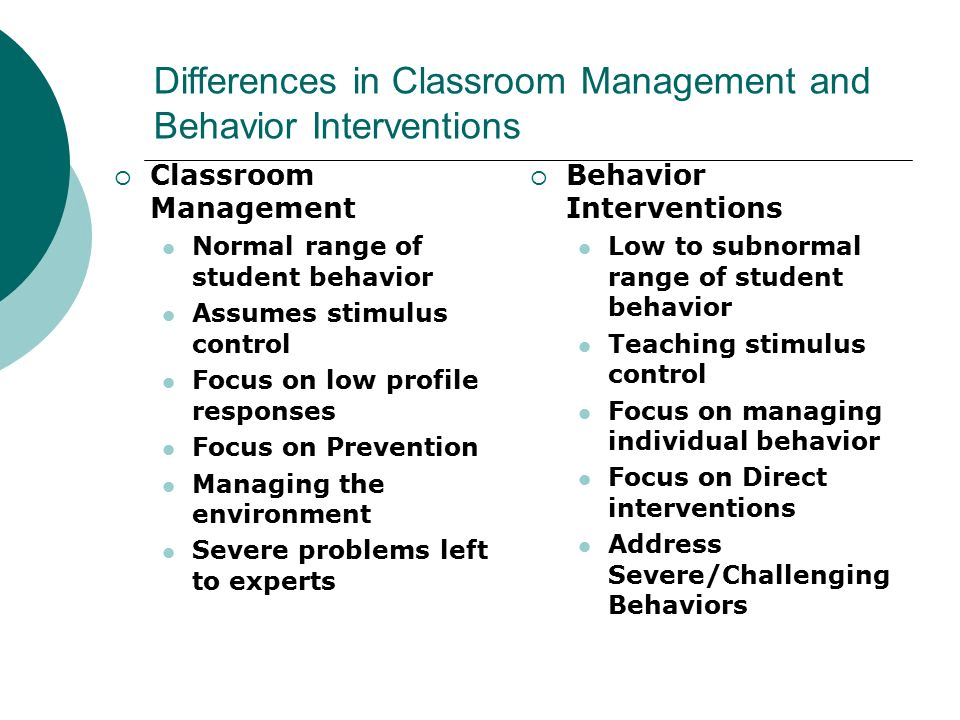
- Scope:
- Classroom Management: Broad in scope, covering all aspects of managing the classroom environment, including physical setup, routines, instructional methods, and student engagement.
- Behavior Management: Narrower in scope, focusing specifically on managing and improving student behavior.
- Focus:
- Classroom Management: Emphasizes creating an overall conducive learning environment through organization, routines, and instructional strategies.
- Behavior Management: Concentrates on promoting positive behavior and addressing behavioral issues through specific interventions and strategies.
- Goals:
- Classroom Management: Aims to establish a well-organized and smoothly functioning classroom where effective teaching and learning can occur.
- Behavior Management: Aims to ensure appropriate student behavior to maintain a safe and orderly learning environment.
- Strategies:
- Classroom Management: Includes a wide range of strategies such as organizing physical space, establishing routines, engaging students, and building relationships.
- Behavior Management: Involves strategies like setting behavioral expectations, using reinforcement and consequences, applying behavioral interventions, and teaching social-emotional skills.
In summary, while classroom management and behavior management are interconnected, they differ in their scope, focus, goals, and strategies. Classroom management is about the overall organization and functioning of the classroom, whereas behavior management specifically targets the regulation and improvement of student behavior.



Leave a Reply